Disclaimer*: The articles shared under 'Your Voice' section are sent to us by contributors and we neither confirm nor deny the authenticity of any facts stated below. Parhlo will not be liable for any false, inaccurate, inappropriate or incomplete information presented on the website. Read our disclaimer.
This article was originally submitted by Mashhood Hamza
‘Care is Better than Cure’- Physician Diary
The Coronavirus Disease is currently a life-threatening health-pandemic; affecting masses around the globe. Currently, COVID-19 is the leading cause of infections related to morbidity and mortality.



via freepik
Current statistics depict that men are more vulnerable in comparison to females. In addition; it has been observed that people falling in age group beyond 40 years with modifiable risk factors; i.e. Diabetes, Hypertension, Obesity, Chronic Obstructive Lung Diseases, are probably more prone to this disease.
The aetiology is defined but symptoms may vary initially starting from fever, mild flue, dry cough, body aches, and abdominal pain or diarrhoea. Some established non-controllable risk factors like age are on the top of the list while some reported cases have shown uncontrolled diabetes may worsen the disease pattern.
Clinically the probability of infected with COVID-19 is considerably low in infants. In contrast, risk of infection significantly increases above 60 years of age due to decline in immunity, pre-existing co-morbid, social gatherings and non-hygienic practices. Symptoms can appear within 05-07 days of the contact with a COVID-19 patient. Moreover, the standard incubation period may vary between 5 and 21 days.
COVID-19 follows somewhat marked ethnic and geographical variations.
The statistical data and information illustrate that mortality risk in African-Americans is higher. Nevertheless, Asians showed an intermediate risk. In contrast, Chinese masses strictly follow precautionary measures directives i.e., isolation, quarantine, hygienic practices, distancing etc.therefore, the possibility of Chinese being infected in the current situation is highly improbable.



via business insider
Genetics can also play a pivot role in immunological behaviour against COVID-19. Countries having lower and lower-middle economies may have more effected people when compared with developed nations. In low economies, people may get affected due to lack of funds, resources, facilities, and awareness. Fewer opportunities and earning is also a substantial problem in these countries.
Likewise, Poor diet, lack of hygiene, social denial for such diseases, psycho-somatic belief on quacks, social gatherings and lack of education are the factors making them prone to get this infection. Some dietary correlation in immune boost up may play a role like certain elements like selenium, zinc, tomatoes and Vitamin E. However, several herbal compounds have the tendency to harm liver and kidneys.
Social gatherings and meetings promote the chances of infectivity and fatality in a defined population.
Also, read What SOPs? Careless Karachites Flood Animal Markets As Eid-Ul-Adha Approaches
Lack of social distancing makes them prone to the spread of infection through aerosols or by shaking hands. On the contrary, wearing facemasks and avoid shaking hands can reduce the infectious spread among the population. The use of carbolic soaps and alcohol-based sanitizers reduces the risk of getting the infection.
The symptoms vary from mild fever and cough to severe respiratory depression leading to multi-organ failures. The pathogenesis initiates by the entry of virus leading to cytokine storm which involves lungs, heart, kidney and liver. Some Researchers suggests the role of the thromboembolic phenomenon and disseminated intravascular coagulation may worsen the condition.



via goodfon
Clinical observation shows that females taking OCPs [oral contraceptive pills] above the age of 40 with COVID-19 positive are at elevated risk of the thromboembolic phenomenon and higher mortality rates relative to Non-OCP users. Patients suffering from liver diseases are at low risk of developing thromboembolic complications.
Proper history and examination are necessary for the virus under strict protection protocols.
These protocols include shifting such patients to COVID-19 Bay and the history of travelling and public interactions. Blood tests like CBC, PT APTT INR, Procalcitonin, CRP, Chest X-Ray may prove helpful; in confirming the infected patient. In the current situation, the suspicious case can only be confirmed by taking nasopharyngeal swabs for rt-PCR.
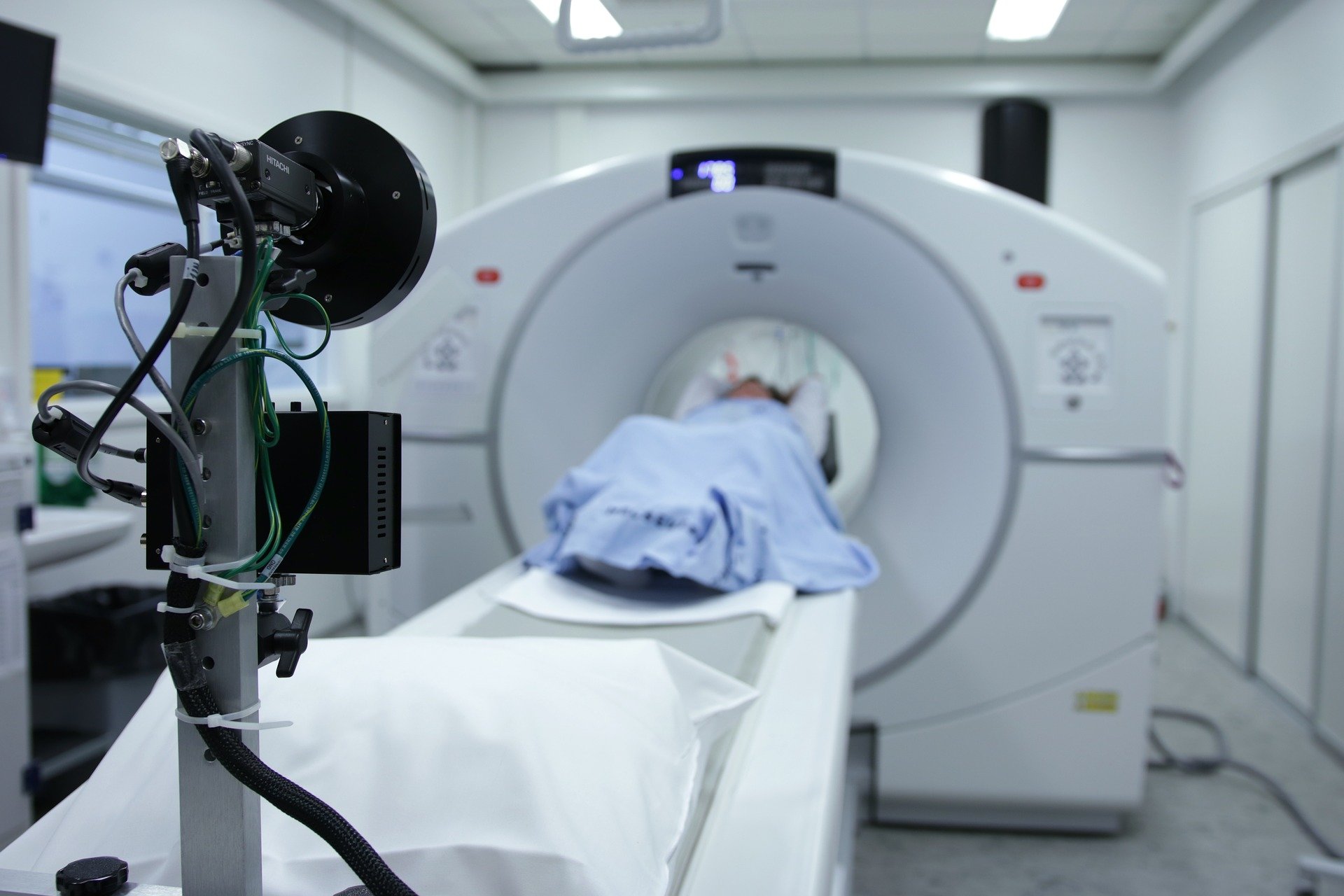
Sometimes patients may contact the emergency department with acute emergency symptoms like severe shortness of breath and respiratory failure or viral septicemia. The patients having the aforementioned symptoms must be triaged and high resonance CT Scan with arterial blood gases be performed urgently for clinical decision making. On the basis of these findings, the rapid decision about respiratory assistance can be made.
The clinical differentiation between the COVID-19 and other febrile illness is a bit tedious and exhausting job. However, after using antibiotics for more than 48 to 72 hours with poor compliance for febrile illness must be subjected to nasopharyngeal swabs for COVID-19 are T.PCR.


via medical Xpress
Presence of ground-glass appearance in Radiological imaging i.e chest CT scan may assist in the diagnosis.
However, this technique may not be useful for all the COVID-19 cases. Furthermore, Coronavirus is curable provided on-time screening and preventive measure is taken into account.
High protein diet, strict glycemic control, regular isolated cardiopulmonary exercises can make the immune system more active and energetic to compete with this lethal virus.
Unfortunately, COVID-19 is currently not curable i.e no FDA registered medicine or vaccines available. Besides, this decease can be prevented. Vaccines and some antivirals are under trials but not succeeded in finding an appropriate drug of choice. Role of Plasma is also under trials but showed some clinically promising recoveries in critical patients.















